Multiple Choice
Why can't ester reduction with lithium aluminum hydride (LAH, LiAlH4) stop at the aldehyde stage?
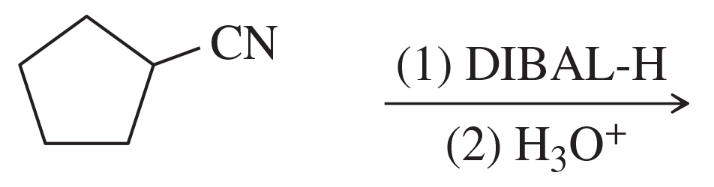
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: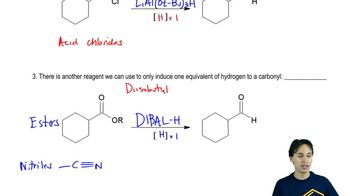

 2:07m
2:07mMaster Why LiAlH4 doesn't work with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning