(i) Which of the following pairs of compounds would you expect to have different physical properties?
(ii) What is the relationship between each of the pairs?
(iii) Assign the absolute configuration of each stereocenter to confirm your answer.
(b)
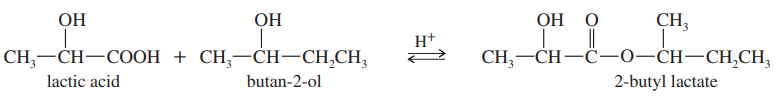
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:41m
1:41mMaster Different atoms or different connectivity. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning