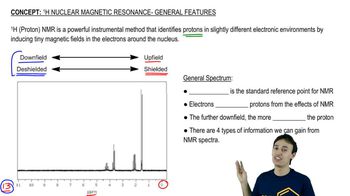
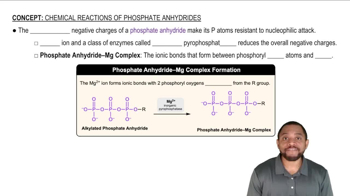
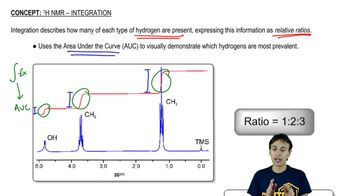
Draw a spectrum for each of the following molecules, being sure to indicate the multiplicity, integration, and chemical shift of each peak. Label each signal based on the set of equivalent hydrogens to which it corresponds.
(c)
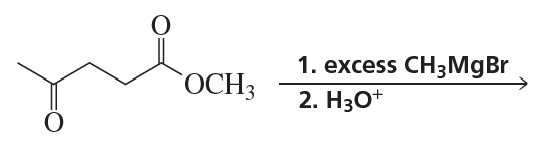
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: