Starting with cyclohexane, how could the following compounds be prepared?
e.
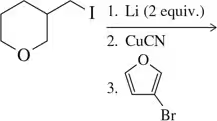
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 13:4m
13:4mMaster Reactions of Organometallics with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning