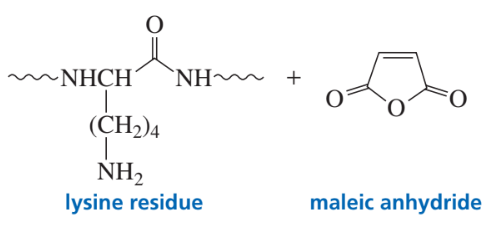
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 9:34m
9:34mMaster Peptides and Polypeptides with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning