Answer Problem 39, parts a–h, using 2-butyne as the starting material instead of propyne.
e. aqueous H2SO4, HgSO4
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: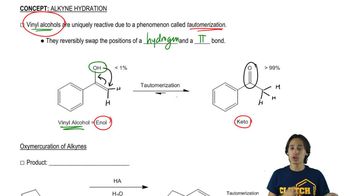



 3:51m
3:51mMaster Vinyl alcohols yield tautomers. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning