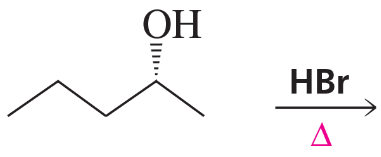
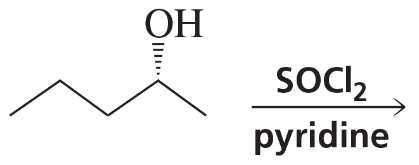
Predict the major products (including stereochemistry) when cis-3-methylcyclohexanol reacts with the following reagents.
(d) concentrated HBr
(e) TsCl/pyridine, then NaBr
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:30m
4:30mMaster Comparing and contrasting the Alcohol Conversions. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning