How would you make the following compounds from N-benzylbenzamide?
c. benzyl alcohol
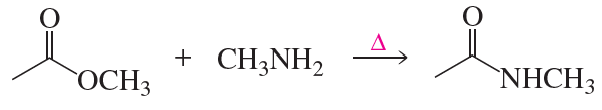
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 9:32m
9:32mMaster NAS - The Three Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning