Textbook Question
Write structural formulas for the following compounds.
(d) divinyl ether
(e) allyl methyl ether
(f) cyclohexene oxide
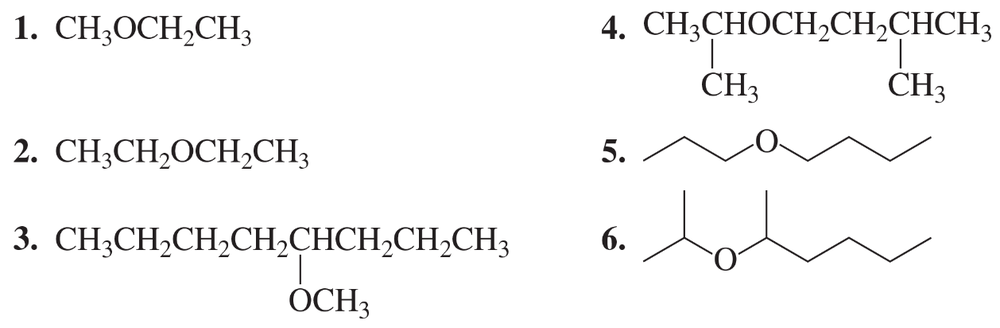
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:32m
1:32mMaster How to name ethers using the common naming system. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning