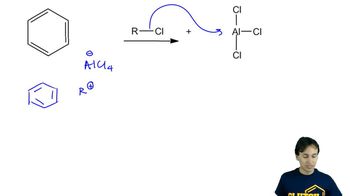
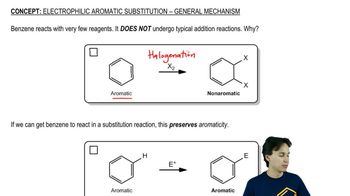
Electrophilic aromatic substitution usually occurs at the 1-position of naphthalene, also called the a position. Predict the major products of the reactions of naphthalene with the following reagents.
(d) isobutylene and HF
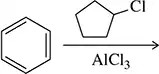
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: