One of these reacts with dilute aqueous acid and the other does not. Give a mechanism for the one that reacts, and show why this mechanism does not work for the other one.
(a)
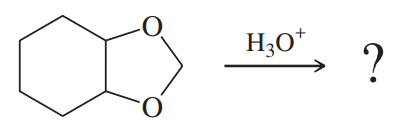
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

