Textbook Question
For each Fischer projection, label each asymmetric carbon atom as (R) or (S).
(e)
(f)
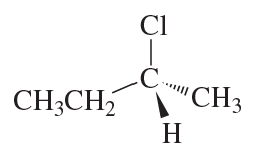
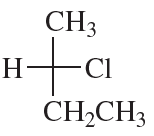
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: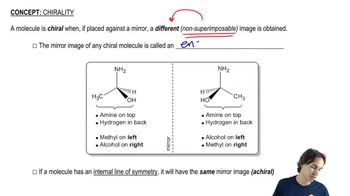

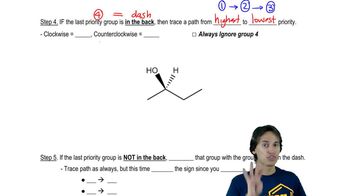

 2:32m
2:32mMaster R and S rule for Fischer Projections. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning