Which nucleophile would be more reactive in the solvent given?
(b)
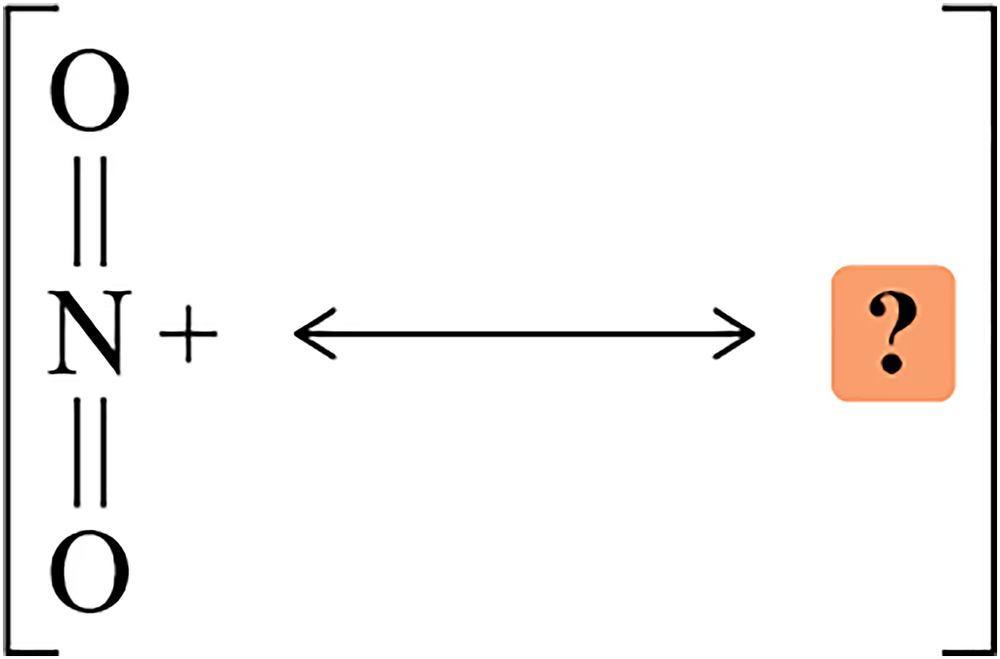
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:21m
6:21mMaster Understanding the difference between basicity and nucleophilicity. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning