What compounds are formed from the reaction of benzoyl chloride with the following reagents?
e. aqueous NaOH
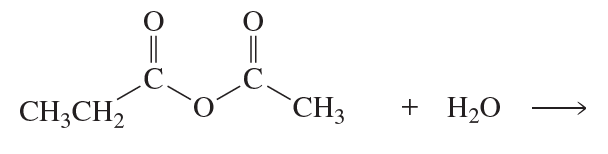
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 9:32m
9:32mMaster NAS - The Three Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning