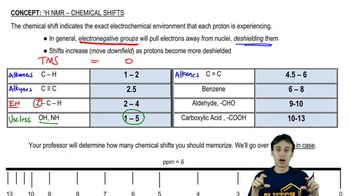
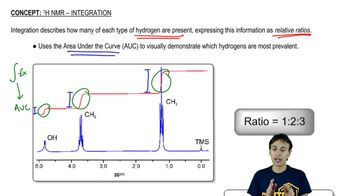
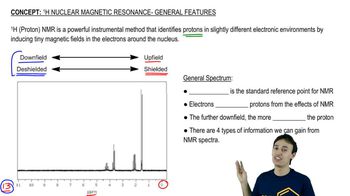
Being able to recognize patterns of integration and multiplicity for common functional groups makes structure identification more efficient. Draw the pattern of integration and multiplicity you'd expect to see for each common alkyl group.
(d)
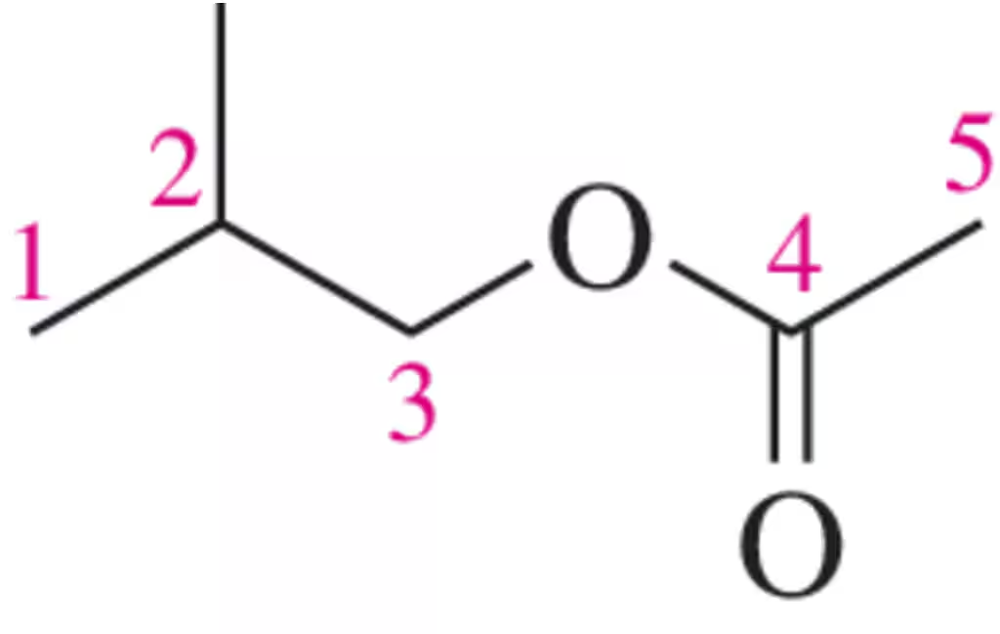
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: