Textbook Question
Show how you would synthesize each compound using methylenecyclohexane as your starting material.
(i)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: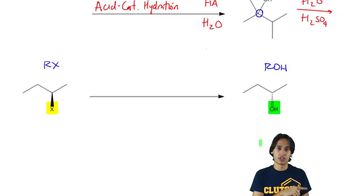
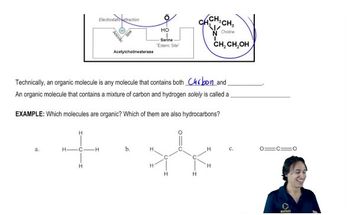
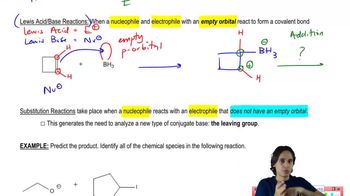

 1:35m
1:35mMaster Moving Functionality in Synthesis with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning