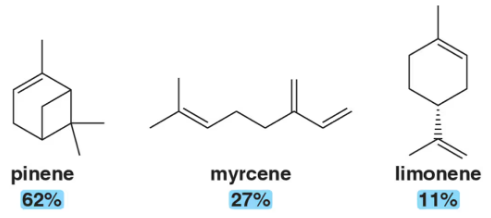
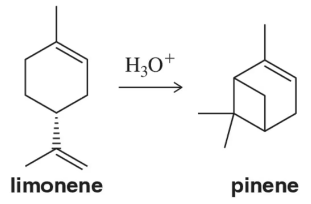
Identify the isoprene units in the terpenes shown. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene.
(e)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 5:29m
5:29mMaster Definition of Conjugation with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning