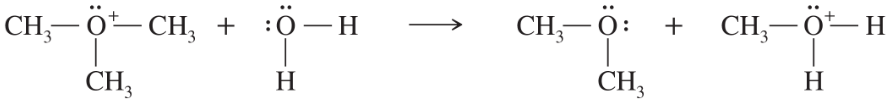
In each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions. Draw any nonbonding electrons to show how they participate in the reactions.
(a)