In Chapter 8, we learned about the chemistry of terpenes and the interesting reactions they can undergo. One such reaction is the acid-catalyzed conversion of nerol to terpineol. Suggest a mechanism for this transformation
.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
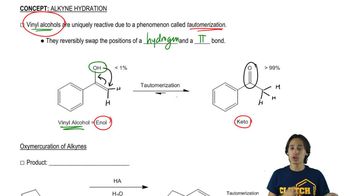


 6:32m
6:32mMaster General properties of acid-catalyzed hydration. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning