Draw a splitting diagram for Hb, where
a. Jba = 12 Hz and Jbc = 6 Hz.
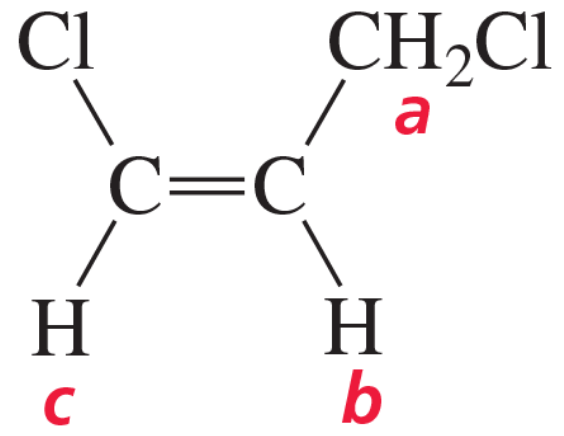
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 8:02m
8:02mMaster Splitting with J-Values:Complex Tree Diagram with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning