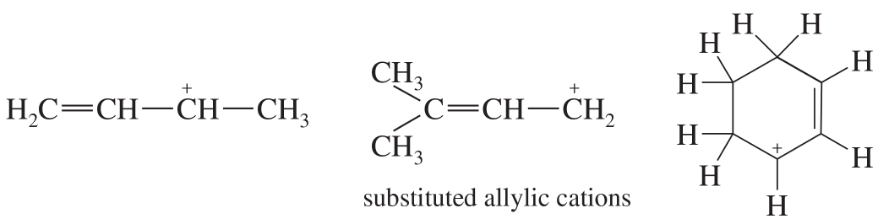
a. Draw resonance contributors for the following species. Do not include structures that are so unstable that their contributions to the resonance hybrid would be negligible. Indicate which are major contributors and which are minor contributors to the resonance hybrid.
b. Do any of the species have resonance contributors that all contribute equally to the resonance hybrid?
13.