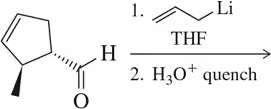
A variety of organometallics, which as strong nucleophiles can react with epoxides, are introduced in Chapter 16. Predict the product of these reactions. [Hint: Assume the carbon–metal bond in each is ionic, with the carbon possessing the negative charge.]
(c)