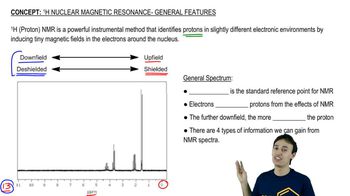
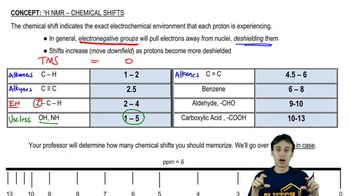
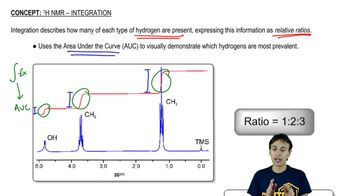
Given the ¹H NMR spectrum and the molecular formula, suggest a structure for each molecule. [The IR spectrum suggests the presence of two C=O bonds.]
(a) Important IR bands (cm ⁻ ¹) : 1728, 1708 [Note: The pKₐ of this molecule is around 10.]
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: