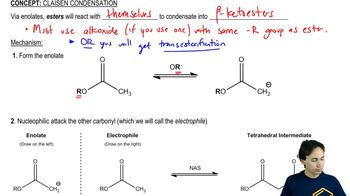
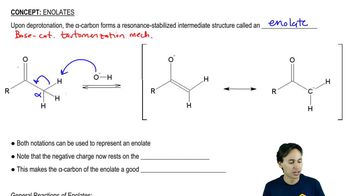
The Knoevenagel condensation is a special case of the aldol condensation in which an active methylene compound reacts with an aldehyde or ketone, in the presence of a secondary amine as a basic catalyst, to produce a new C=C. Show the starting materials that made each of these by a Knoevenagel condensation.
(a)