Textbook Question
Draw the correct structure from the following IUPAC names:
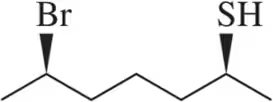
(e) (R)-2,2-dimethyl-1-phenylpropane-1-thiol
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:34m
5:34mMaster How to name sulfur-containing compounds. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning