Textbook Question
What two carbonyl compounds are required for the synthesis of morachalcone A, via a Claisen–Schmidt condensation?
<IMAGE>
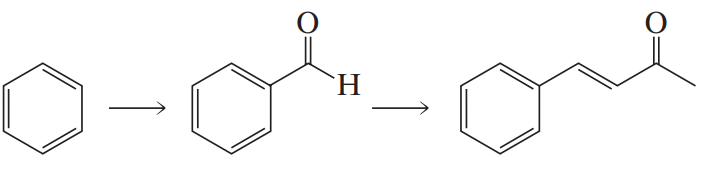
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: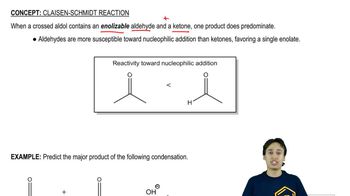

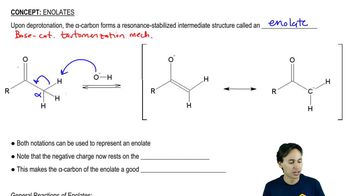

 2:10m
2:10mMaster Claisen-Schmidt Reaction with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning