Textbook Question
Draw the substitution products for each of the following reactions; if the products can exist as stereoisomers, show what stereoisomers are obtained:
a. (R)-2-bromopentane+CH3O−
b. (R)-3-bromo-3-methylheptane+CH3OH
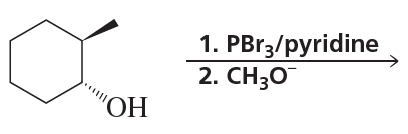
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 3:32m
3:32mMaster How do we predict if the mechanism is SN1 or SN2? with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning