Draw the product(s) of each of the following reactions:
a. benzoic acid + HNO3/H2SO4
b. isopropylbenzene + Cl2 + FeCl3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: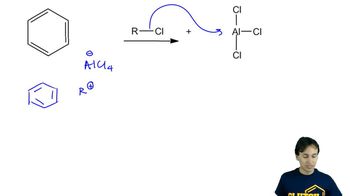
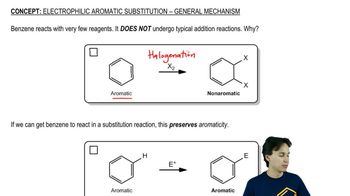


 4:29m
4:29mMaster Activity and Directing Effects with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning