Develop syntheses for the following compounds. As starting materials, you may use cyclopentanol, alcohols containing no more than four carbon atoms, and any common reagents and solvents.
(e)
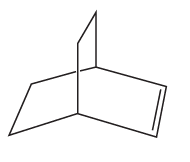
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 0:24m
0:24mMaster Intro to Predict the Product with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning