Predict the major products of the following reactions.
a. 1-methylcyclohexene+ aqueous Hg(OAc)2
b. the product from part (a), treated with NaBH4
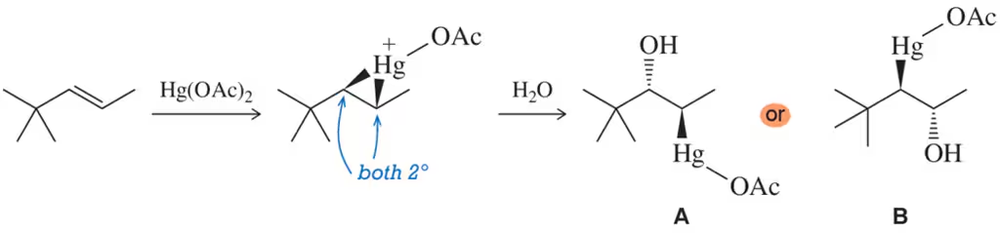
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 5:m
5:mMaster General properties of oxymercuration-reduction. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning