For the following compounds, which pairs of hydrogens (Ha and Hb) are enantiotopic hydrogens?
1.
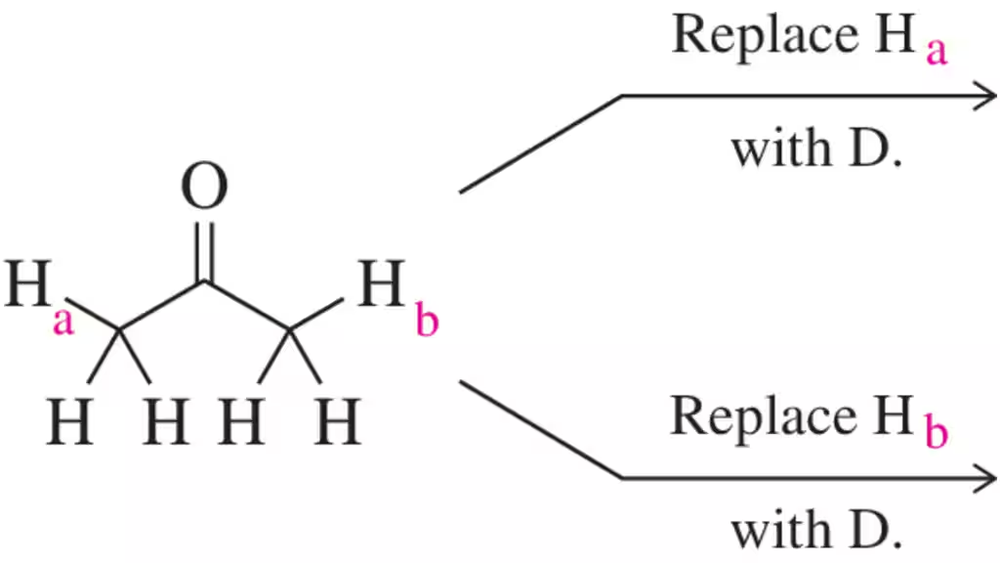
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: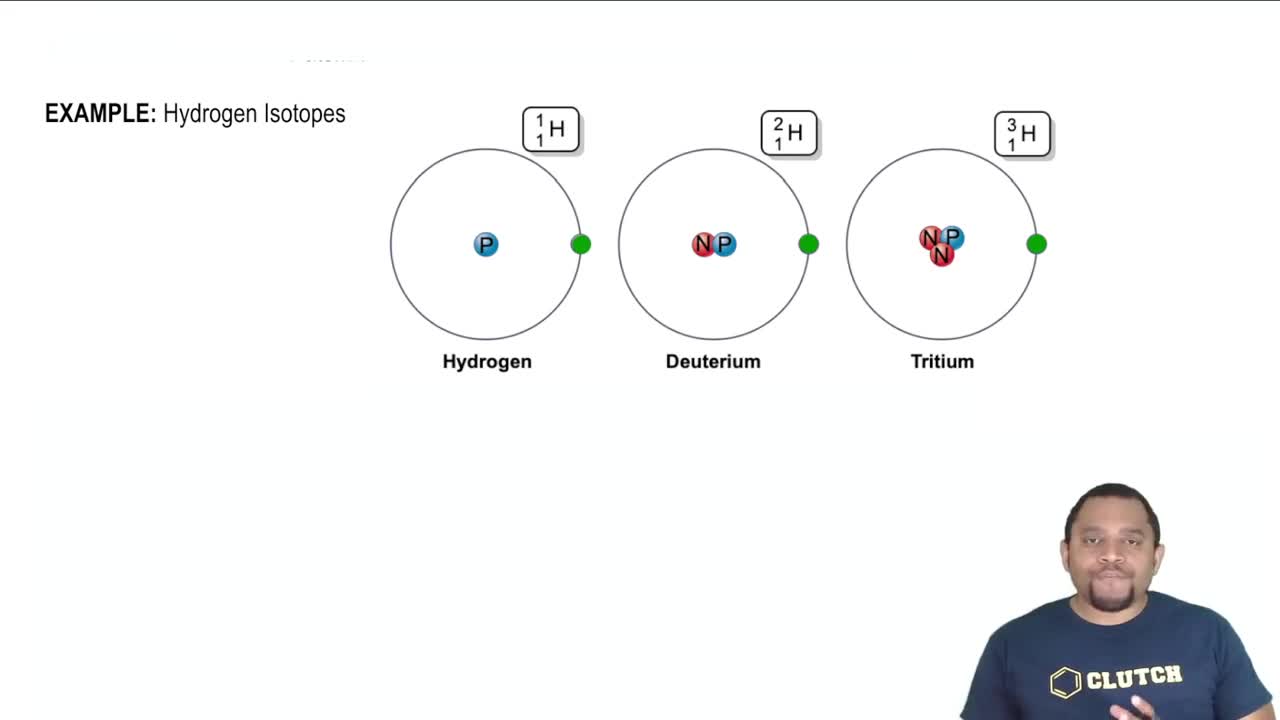
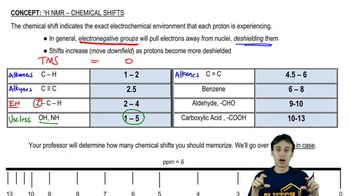
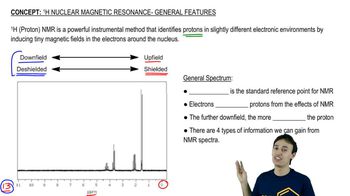

 11:4m
11:4mMaster Q-Test (Proton Relationships) with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning