Recall (Section 16-10) that two positions of anthracene sometimes react more like polyenes than like aromatic compounds.
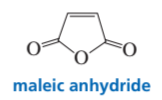
b. The Diels–Alder reaction of anthracene with maleic anhydride is a common organic lab experiment. Predict the product of this Diels–Alder reaction.