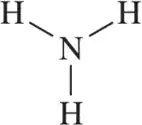
Draw the Lewis structure for the following ions. Be sure to calculate the formal charge of each atom to confirm that your structure is correct.
(b) H+
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:34m
1:34mMaster Calculating formal and net charge. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning