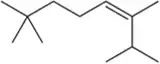
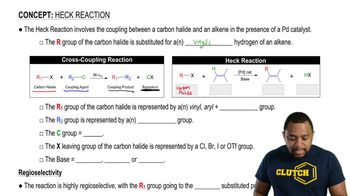
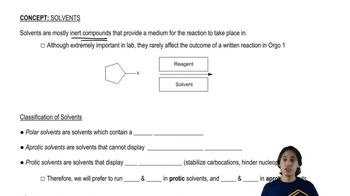
At the beginning of Chapter 9, we stated that after finishing Chapters 8 and 9, we would have the ability to make a large variety of functional groups using related reactions. Show the reagent(s) necessary to convert 1-isobutylcyclohexene into the following molecules.
(c)