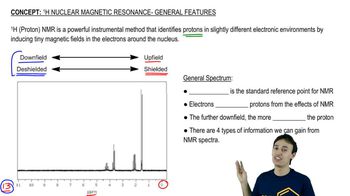
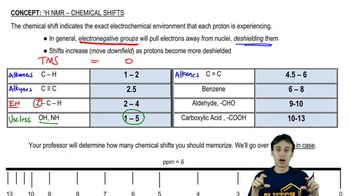
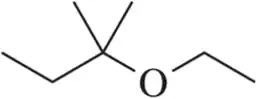In the lab, ¹H NMR is often used to verify that a reaction has worked as expected by comparing the product spectrum with what is expected. Given the ¹H NMR of the reactant shown, draw the spectrum you'd expect to see of the product that results.
<IMAGE>