Which set of underlined hydrogens has its 1H NMR signal at a higher frequency?
a. CH3CH2CH3 or CH3OCH2CH3
b. CH3CH=CH2 or CH3OCH=CH2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: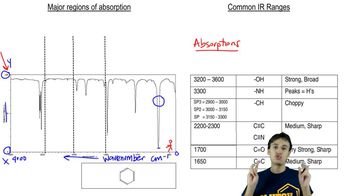
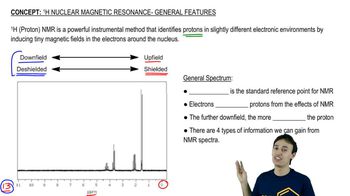
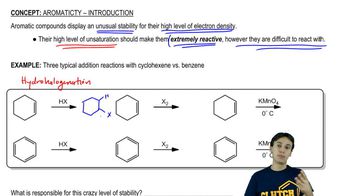

 11:44m
11:44mMaster 1H NMR Chemical Shifts with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning