(+)-Mandelic acid has a specific rotation of +158. What would be the observed specific rotation of each of the following mixtures?
c. 75% (-)-mandelic acid and 25% (+)-mandelic acid
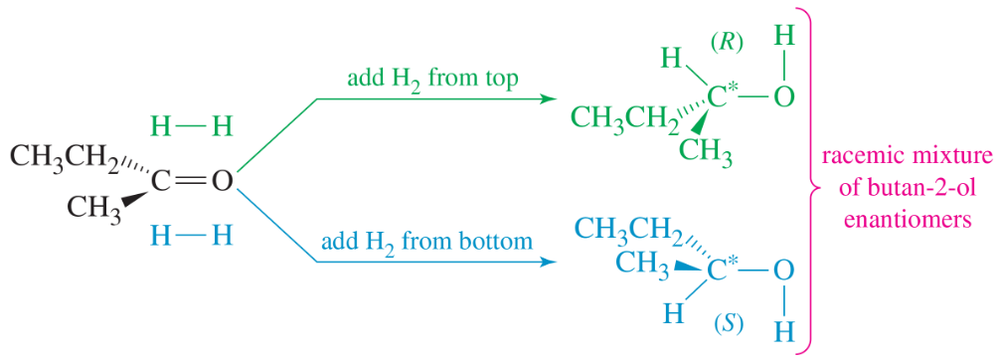
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:21m
4:21mMaster How to calculate enantiomeric excess. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning