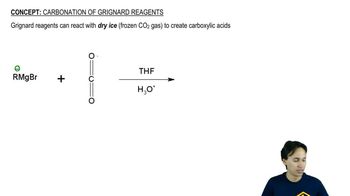
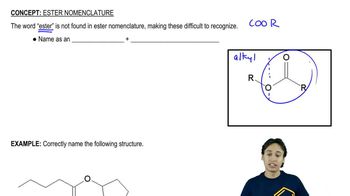
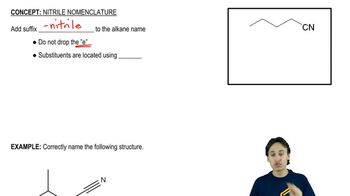
Show how each transformation may be accomplished by using a nitrile as an intermediate. You may use any necessary reagents.
(b) cyclohexanecarboxamide → cyclohexyl ethyl ketone
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: