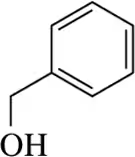
When using sulfuric acid, but in the absence of other nucleophiles like water or bromide ion, less stable alkenes can be isomerized to their more stable isomer. Provide a mechanism for these acid-catalyzed isomerization reactions. [This is one illustration of the principle of microscopic reversibility.]
(a)