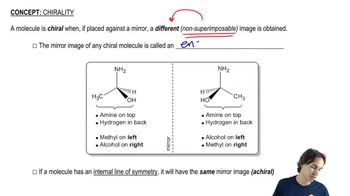
Which of the following has an achiral stereoisomer?
i. 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
j, 1,2-dimethylcyclobutane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: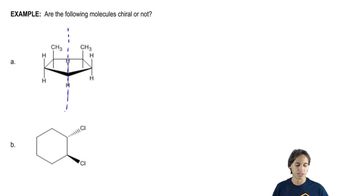


 3:52m
3:52mMaster Three types of disubstituted cycloalkanes with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning