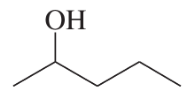
Multiple Choice
Predict the major organic product of the following reaction.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: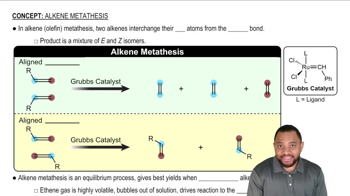
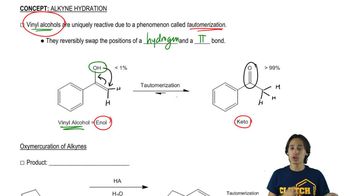

 2:26m
2:26mMaster Forming alcohols through Oxymercuration-Reduction. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning