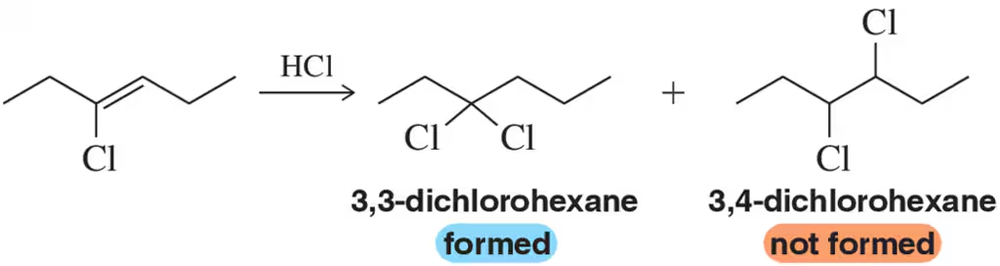
Suggest an alkene that, upon reaction with the appropriate hydrohalic acid, will produce only the alkyl halide shown. [Ignore stereochemistry.]
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 4:07m
4:07mMaster General properties of hydrohalogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning