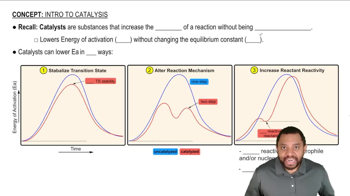
Starting from bromobenzene and any other reagents and solvents you need, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. Any of these products may be used as starting materials in subsequent parts of this problem.
d. 3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ol
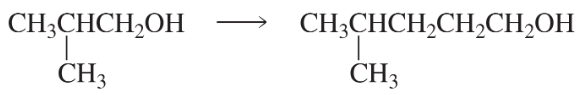
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: