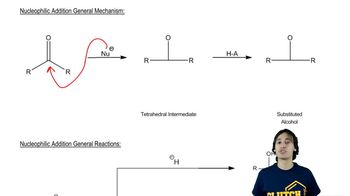
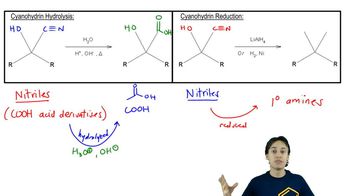
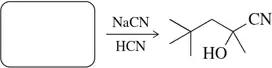
Identify the bonds broken and formed in the following addition reaction.
(a) Would you expect this reaction to be favored based on entropy?
(b) Based on enthalpy [qualitatively]?
(c) Overall?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: