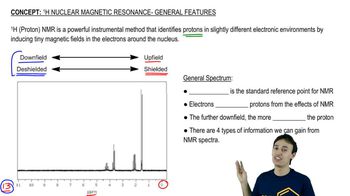
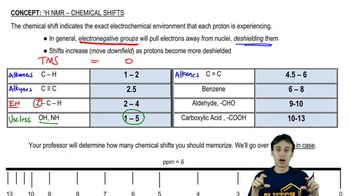
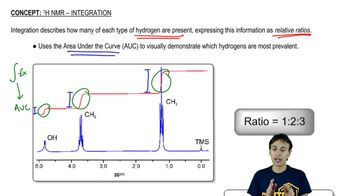
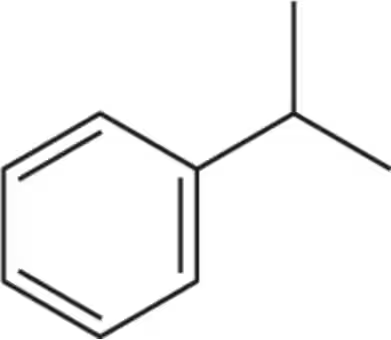
For the following molecules, give the integration you would expect for the signal associated with the hydrogens at the labeled carbons. [Pay attention to the symmetry, or lack of symmetry, in the molecules.]
(e)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: