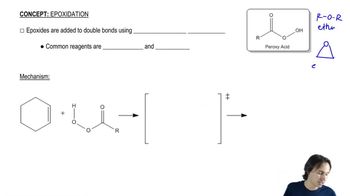
Develop syntheses for the following compounds. As starting materials, you may use cyclopentanol, alcohols containing no more than four carbon atoms, and any common reagents and solvents.
(a) trans-cyclopentane-1,2-diol
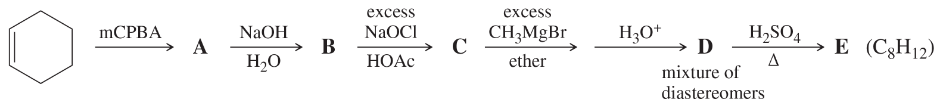
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: