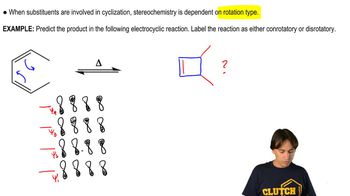
a. Identify the mode of ring closure for each of the following electrocyclic reactions
2.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: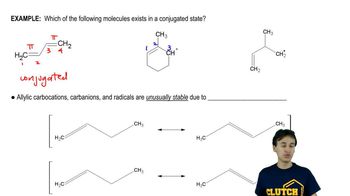
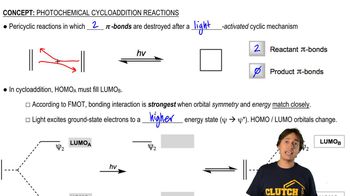

 5:51m
5:51mMaster Two Steps to Predicting Any Electrocyclic Products with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning