The following compounds can all react as bases.
c. Rank the original compounds in order, from strongest base to weakest base.
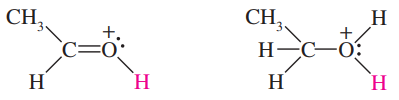
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 9:36m
9:36mMaster The 12 pKa values you want to memorize (because they are important!). with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning