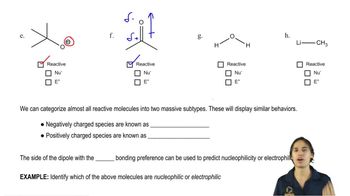
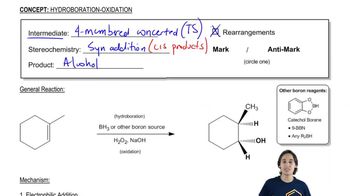
The bulky borane 9-BBN was developed to enhance the selectivity of hydroboration. In this example, 9-BBN adds to the less hindered carbon with 99.3% regioselectivity, compared with only 57% for diborane.
b. 9-BBN is synthesized by adding BH3 across a symmetric, cyclic diene. What is the structure of the diene?