When 2,2-dibromo-1-phenylpropane is heated overnight in fused KOH at 200 C, the major product is a foul-smelling compound of formula C9H8. Propose a structure for this product, and give a mechanism to account for its formation.
Problem-Solving Hint:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: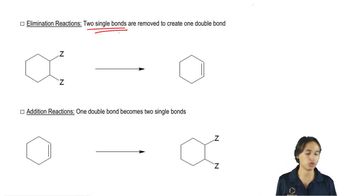


 2:20m
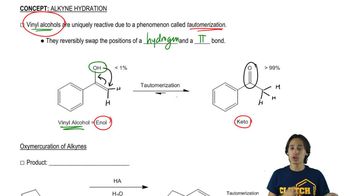
2:20mMaster General features of double dehydrohalogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning